Carbonate Buffer System In Ocean
Then you will look at the role carbonate and hydrogencarbonate ions play in this buffering process. The bicarbonates in the seawater used for scrubbing act to neutralise or buffer the solution by consuming.
One that is important in surface waters is the carbonic acidbicarbonate buffer.

Carbonate buffer system in ocean. People also ask what is the buffer in the ocean. Seawater can resist drastic pH changes even after the addition of weak bases and acids. In this experiment you will compare the way seawater and fresh water buffer carbon dioxide gas.
Consequently global estimates of DIC delivery to the ocean can be used as a proxy for alkalinity transfer from weathering to the ocean. Review introductory information on the NOAA Ship. The carbonate system encompasses virtually all of the environmental compartments the atmosphere hydrosphere biosphere and as CaCO 3 major parts of the lithosphere.
A Brief Summary of Carbonate Buffer System Chemistry. Use this video micro-lecture explains carbonate buffering in the ocean. Carbonate system is the primary buffer for the acidity of water which determines the reactivity of most chemical compounds and solids.
These are photosynthetic organisms so they remove CO 2 from the ocean-atmosphere system as they produce the organic molecules that sustain their life. The rapid decrease in this buffer capacity suggests that while the ocean will likely continue to take up more CO 2 in the future due to the increasing atmospheric CO 2 concentrations the proportion of anthropogenic carbon dioxide entering the ocean will decrease. The carbonate system which is the major source of bufiering in the ocean and is the main subject of this chapter.
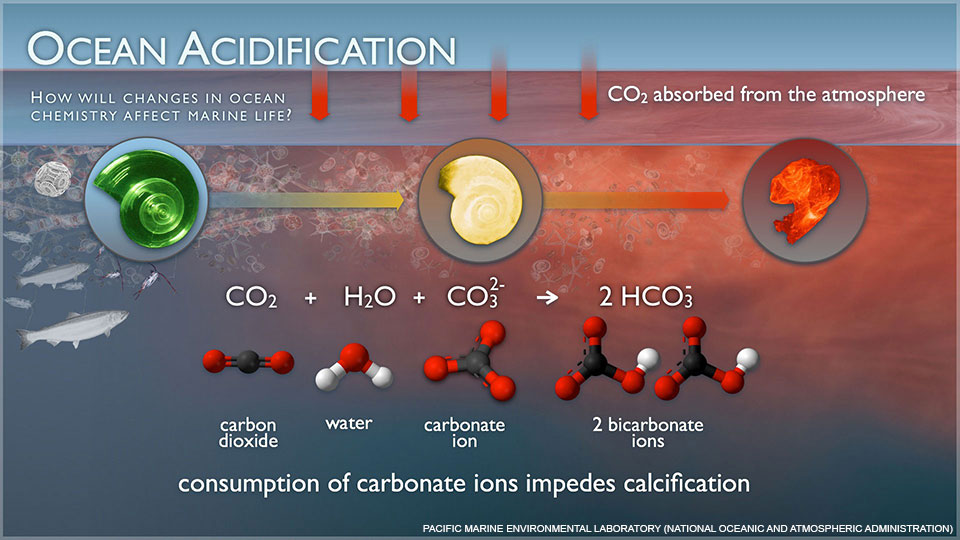
CO2 atmos CO2aqH2O H2CO3 HHCO3- 2HCO32-. Calcium carbonate CaCO 3 is a very common mineral. Atmospheric CO 2 dissolves in seawater and is hydrated to form carbonic acid H 2 CO 3.
That is it can undergo two de-protonation reactions to form bicarbonate HCO 3- and carbonate CO 3 2-. With the sole exception of the chemistry of water itself this is by far the most complex equilibrium system and it touches upon every aspect of the Earth sciences-meteorology geology oceanography and certainly biology. Regulation the CO2 content of the atmosphere via the biological pump.
In other words calcium carbonate acts to neutralise or buffer the solution by consuming hydrogen ions 8. They also take in Ca 2 aq and HCO 3 aq ions from the surrounding sea to synthesize the intricate CaCO 3 scales that adorn their exterior. This means that there is an excess of H ions in the ocean and the pH of the ocean has been.
Likewise what is the pH of the Ocean 2019. Over the past twenty years accurate measurement of the seawater carbon dioxide system has become a high priority for scientists who have worked to understand just how much of the carbon dioxide CO 2 created by mans activities has ended up in the ocean where it is distributed and how it has changed the chemistry of the oceans. It is central to.
To prepare for this lesson. This lesson guides a student investigation into some properties of the oceans carbonate buffer system and how changes in atmospheric carbon dioxide levels may affect ocean pH and biological organisms that depend upon calcification. Carbonate Buffers Recall that buffers are mixtures of weak acids and their conjugate bases that resist changes in pH.
What would happen if the amount of CO 2 in the atmosphere were to sharply rise. One of the most important systems in the oceans is the CO2-carbonate system a buffering system that helps to maintain the pH of seawater to within a narrow range. The bicarbonate and carbonate ions are responsible for the buffering capacity of seawater ie.
The relationship between the components in the oceans buffer system can be represented by the equation below. NIWA 2016 states that this natural buffering ability that the ocean possesses is called a carbonate buffer system. Ocean must continue to buffer an increasing amount of carbon dioxide.
Similarly calcium and magnesium bicarbonates which are present in seawater at a concentration of approximately 140 mgl 11 consume free hydrogen ions decreasing hydrogen ion activity ie. The control of seawater pH. The co-existence of these species in seawater creates a chemical buffer system regulating the pH and the pCO 2 of the oceans.
Carbonate burial estimates range from 18 to 34 Tmol C year 1 supporting information S3 with clear consensus about carbonate burial in the deep sea of 1112 Tmol C year 1 while ocean margin contributions vary from 6 to 23 Tmol C year 1 Iglesias. That is it can undergo two de-protonation reactions to form bicarbonate HCO 3- and carbonate CO 32-. The CarbonateBicarbonate buffer system is an important way for the ocean to maintain chemical equilibrium.
The increased atmospheric CO 2 as a result of burning fossil fuels has driven this entire reaction to far to the right. It also briefly discusses the change in the chemical composition of the ocean caused by a higher concentration of dissolved CO2 and the resulting effect on ocean biota. Carbonic acid is divalent.
Ocean Carbonate System Carbonate chemistry is the most intensely studied subject of marine chemistry. Limestone is one familiar form of calcium. This is a series of reactions in which dissolved CO 2 is converted to bicarbonate using carbonate as a buffer that has kept the level of H protons and therefore pH constant.
Carbonic acid is divalent. Buffering atmospheric carbon dioxide Equipment 150 mL seawater. The carbonate system of the ocean plays a key role in controlling the pressure of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere which helps to regulate the temperature of the planet.
In natural systems there are many buffers. The oceans role in buffering global climate change will gradually diminish and ocean acidification could accelerate. The carbonate buffer system For the last 750000 years the pH of the surface ocean has been relatively stable and slightly alkaline at 82 due to the carbonate buffer system.
Carbonate System 1 1 MAR 510 Chemical Oceanography Carbonate Equilibrium-Key Concepts- Major buffer system influencing pH master variable Linked to geological biological and climatological cycles Complex chemistry involving gaseous dissolved and solid phases. Further use the video micro-lecture to illustrate Le Chateliers Principleexplain. Lecture 10 - Acids and Bases.
Seawater naturally has a higher pH than the equilibrium constant of water and the main buffers besides water itself are the carbonate system bicarbonate HCO3- carbonate HCO32- with.

Marine Reserves Can Mitigate And Promote Adaptation To Climate Change Climate Change Marine Reserves Climates

Policy Brief Emerging Ocean Acidification Threatens Baltic Sea Ecosystems Baltic Eye

Ocean Chemistry Acidification Time Scavengers
Western Arctic Log What Is Ocean Acidification

Coccolithophore Carbon Chemistry Carbon Cycle Diatom Ocean Acidification

Ocean Chemistry Acidification Time Scavengers

Aquaponics Ph Explained How To Maintain The Perfect Balance Aquaponics Well Water System Solid Shampoo Bar
Ocean Acidification Point Reyes National Seashore U S National Park Service

Ocean Chemistry Acidification Time Scavengers

Global Shallow Water Ocean Carbonate Model Socm At Steady State Year Download Scientific Diagram



Posting Komentar untuk "Carbonate Buffer System In Ocean"