Carbonate Buffer System In Seawater
One of the most important systems in the oceans is the CO2-carbonate system a buffering system that helps to maintain the pH of seawater to within a narrow range. It is central to.
Buffering atmospheric carbon dioxide Equipment 150 mL seawater.

Carbonate buffer system in seawater. The control of seawater pH. This is the solubility product of calcium carbonate. The higher the value of the carbonates the less the pH value will be affected by acidic substances.
It also briefly discusses the change in the chemical composition of the ocean caused by a higher concentration of dissolved CO2 and the resulting effect on ocean biota. 3 2 Na CO3 NaCO 3 3. The carbonic acid system dominates the buffering capacity of seawater and these sensitivities thus show extrema related to the pK 1 59 and pK 2 9 values of carbonic acid in seawater.
Carbonate system in seawater is confirmed experimentally as 00114 pH units per degree Celsius at 1 atm pressure. The carbonate hardness stabilizes the pH value of. Carbon dioxide plays a vital role in the chemistry of sea water.
In other words calcium carbonate acts to neutralise or buffer the solution by consuming hydrogen ions 8. For the last 750000 years the pH of the surface ocean has been relatively stable and slightly alkaline at 82 due to the carbonate buffer system. Systems such as phosphoric acid-phosphate hydrogen phosphate play a limited role.
Carbonate buffer system in seawater. With the sole exception of the chemistry of water itself this is by far the most complex equilibrium system and it touches upon every aspect of the Earth sciences-meteorology geology oceanography and. The bicarbonates in the seawater used for scrubbing act to neutralise or buffer.
When the first proton is donated HCO3- otherwise known. As CO 2 increases in seawater it produces carbonic acid which dissolves CaCO 3 shells such as foraminifera. Similarly calcium and magnesium bicarbonates which are present in seawater at a concentration of approximately 140 mgl 11 consume free hydrogen ions decreasing hydrogen ion activity ie.
Ocean Carbonate System Carbonate chemistry is the most intensely studied subject of marine chemistry. Lecture 10 - Acids and Bases. Journal of Marine Systems 5 111-118.
These interactions can be described in terms of an ion association formalism and more recently in terms of a specific interaction theory Mil96 Stu81. Ocean must continue to buffer an increasing amount of carbon dioxide. Then you will look at the role carbonate and hydrogencarbonate ions play in this buffering process.
In this experiment you will compare the way seawater and fresh water buffer carbon dioxide gas. Dissolved O 2 CO 2. And Liu Y-M 2010 The universal ratio of the boron to chlorinity for the North Pacific and North Atlantoc oceans.
The carbonate ion can react with calcium ions Ca which are in excess in. The sensitivity shows maxima at pH values of about 45 and 75. The package was subsequently upgraded.
Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 74 1801-1811. In tissues and blood the CO 2 bicarbonate buffer system is distinguished from non-bicarbonate buffers when analysing the titration of the latter by accumulating CO 2 by metabolic infl uences or during proton-equivalent ion exchange. For the case of a fixed partial pressure of carbon dioxide and calcium carbonate dissolved in the aqueous phase one more equation is need to describe the system.
The carbonate hardness in the aquarium consists mainly of the buffer system carbon dioxide-carbonic acid hydrogen carbonate-carbonate. The bicarbonate and carbonate ions are responsible for the buffering capacity of seawater ie. Further use the video micro-lecture to illustrate Le Chateliers Principle.
K CaCO Ca CO o CaCO 3 2 - 3 2 3 19. The generated values of pH have also been used to relate the two scales at various temperatures PHNBS PH-Tri A Bt 20 lO3 593 - 36S - 35 20a lO 3381 00585 - 35 20b The differences between the two buffer scales are The thermodynamics of the carbonate system in seawater 1659 Table 7. Acid in seawater and titratable acidity by use of strong base in physiological fl uids like urine.
As for boron it accounts for about 10 of the buffering capacity and is present mostly as borate BOH 4. The carbonate system encompasses virtually all of the environmental compartments the atmosphere hydrosphere biosphere and. That is it can undergo two de-protonation reactions to form bicarbonate HCO 3- and carbonate CO 3 2-.
Carbonic acid is divalent. O system Calcium carbonate in water with a fixed partial pressure of carbon dioxide. The carbonate system which is the major source of bufiering in the ocean and is the main subject of this chapter.
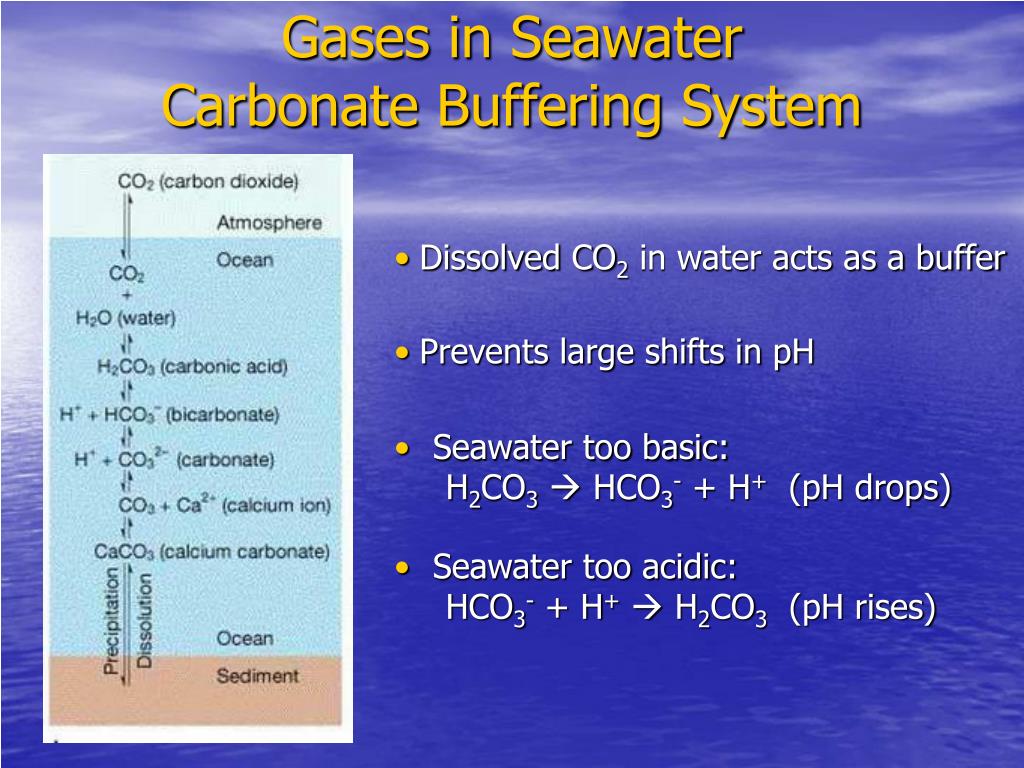
In 2008 a new version 20 was built with the assistance of Héloïse Lavigne. A Brief Summary of Carbonate Buffer System Chemistry Atmospheric CO 2 dissolves in seawater and is hydrated to form carbonic acid H 2 CO 3. In 2003 Aurélien Proye and I put together seacarb an R package that calculates various parameters of the carbonate system in seawater.
Although pH measurements with a given system are repro- ducible to -c-O005 or 20006 pH units direct pH measurements on seawater are accurate. When atmospheric carbon dioxide is dissolved in seawater carbonic acid H 2 CO 3 is formed. The carbonate buffer system.
The carbonate system in seawater is characterised by the interaction of major cations Na Mg2 Ca2 and K and major anions Cl- SO 4 2- HCO 3-and CO 3 2-. The CarbonateBicarbonate Buffer System. Lee K Tae-Wook K Byrne RH Millero FJ Feely RA.
Regulation the CO2 content of the atmosphere via the biological pump. This is a series of reactions in which dissolved CO 2 is converted to bicarbonate using carbonate as a buffer that has kept the level of H protons and therefore pH constant. Frankignoulle M 1994 A complete set of buffer factors for acidbase CO2 system in seawater.
Determining the oceans influence on fossil fuel CO2 uptake. Use this video micro-lecture explains carbonate buffering in the ocean. Vertical profiles in Pacific Atlantic.
Seawater can resist drastic pH changes even after the addition of weak bases and acids. The buffer capacity of the seawater will not change because the main chemical reaction triggered by the outgassing of CO2 is HCO 3- H ---- H 2 O CO 2 which leaves the alkalinity unchanged. Unfortunately carbonate is mostly unstable in seawater and can readily combine with dissolved calcium magnesium and some trace elements and precipitate out of solution.
Carbonic acid is diprotic which means in has two H ions to donate to solution.

Ocean Chemistry Acidification Time Scavengers
How Does Seawater Buffer Or Neutralize Acids Created By Scrubbing Egcsa

Climate Change Education Across The Curricula Across The Globelesson Plan Buffers Buffer Action And Ocean Acidification

Ocean Chemistry Acidification Time Scavengers

The Carbonate System In Seawater And Its Response To Increased Download Scientific Diagram

Ocean Chemistry Acidification Time Scavengers

Chemical Oceanography Lecture 3 5 30 2014 Salinity Definition Weight Of Inorganic Salts In One Kg Of Seawater There Are Many Ions And Salts In Seawater Ppt Download
Chapter 5c Dissolved Gases In Seawater
Ppt Ocean Water Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 6799987

Carbonate Buffering And Metabolic Controls On Carbon Dioxide In Rivers Stets 2017 Global Biogeochemical Cycles Wiley Online Library

Ocean Chemistry Acidification Time Scavengers



Posting Komentar untuk "Carbonate Buffer System In Seawater"