Bicarbonate Buffer System
Bicarbonate buffer system The pH of a solution ultimately depends on the concentration of H ions in the solution. Bicarbonate buffer- Has the following limitations.

Bicarbonate Buffer System And Ph Imbalances Part 1 Nursing School Notes Nursing Videos Icu Nursing
This means that there is an excess of.

Bicarbonate buffer system. The CarbonateBicarbonate buffer system is an important way for the ocean to maintain chemical equilibrium. The bicarbonate buffer system plays a vital role in other tissues as well. If you give two liters of isotonic bicarbonate this can increase the extracellular fluid volume by 15.
Renal physiology controls pH levels through several powerful mechanisms that excrete excess acid or base. After carbon dioxide is dissolved it combines with the water molecules to form. The bicarbonate buffer system plays a vital role in other tissues as well.
In the body a bicarbonate buffer system is used to regulate the pH of blood. The pK for the phosphate buffer is 68 which allows this buffer to function within its optimal. Cannot protect the ECF from pH changes due to increased or depressed CO2 levels Only functions when respiratory system and control centers are working normally It is limited by.
The carbonic acid - bicarbonate buffer system consists of carbonic acid a weak acid and the bicarbonate anion its conjugate base. In the human stomach and duodenum the bicarbonate buffer system serves to both neutralize gastric acid and stabilize the intracellular pH of epithelial cells via the secretion of bicarbonate ion into the gastric mucosa. The extracellular fluid volume of a mean baking soda manufacturers person is about 14 liters.
This reaction then takes the aqueous carbon dioxide gas and dissolves it in the liquid water in order to combine and produce aqueous carbonic. Isotonic bicarbonate is generated by adding 150 mEq of sodium bicarbonate eg. Changing the concentration by the addition or removal of H ions can impact the pH of a solution.
Using optical traps to manipulate single DNA strands. Bicarbonate Buffer System and pH Imbalances - YouTube. The bodys chemical buffer system consists of three individual buffers.
The bicarbonate buffering system is an crucial buffer system in the acid-base homeostasis of all living things. Other buffers perform a more minor role than the carbonic-acid-bicarbonate buffer in regulating the pH of the blood. While the third buffer is the most plentiful the first is usually considered the most important since it is coupled to the respiratory system.
The carbonatecarbonic acid buffer the phosphate buffer and the buffering of plasma proteins. The bicarbonate buffer system plays a vital role in other tissues as well. The bicarbonate buffer is the primary buffering system of the IF surrounding the cells in tissues throughout the body.
What is the bicarbonate buffer system and what is it used for. In this video Dr Mike explains how the bicarbonate buffer system controls pH changes. The bicarbonate buffer system is the main buffering system used in the body.
Three 50-mEq ampules to a liter of 5 dextrose. Bicarbonate Buffer System and pH Imbalances. The bicarbonate buffering system is an crucial buffer system in the acid-base homeostasis of all living things.
The important thing to realize here is that carbonic acid H 2CO3 is actually formed when carbon dioxide CO2 is dissolved in water. As mentioned the bicarbonate buffer represents a powerful tool for modulating total ECF pH because the Weak Acid and Weak Base forms of the buffer can be independently controlled. The influence of the bicarbonate-carbon dioxide buffer system on the pH gradient delta pH across the inner membrane of mitochondria from rabbit renal cortex was studied with and without phosphate in the medium.
In the human stomach and duodenum the bicarbonate buffer system serves to both neutralize gastric acid and stabilize the intracellular pH of epithelial cells via the secretion of bicarbonate ion into the gastric. This system relies on a dual equilibrium process where cellular respiration produces aqueous carbon dioxide gas and liquid water. The ECF partial pressure of the Weak Acid form Pa CO 2 can be controlled by changing rates of alveolar ventilation as explained in Respiratory Acid-Base Control.
The main role of the bicarbonate system is to regulate and control the pH of blood and counteract any force that will alter the pH. The phosphate buffer consists of phosphoric acid H 3 PO 4 in equilibrium with dihydrogen phosphate ion H 2 PO 4- and H. Other pH-Buffer Systems in the Blood.
The role of the bicarbonate buffer system in regulating blood pH This is the currently selected item. The respiratory and renal systems also play major roles in acid-base homeostasis by removing CO 2 and hydrogen ions respectively from the body. The bicarbonate buffering system maintains optimal pH levels and regulates the carbon dioxide concentration that in turn shifts any acidbase imbalance.
The Carbonic AcidBicarbonate Buffer. The bicarbonate buffer system is an acid-base homeostatic mechanism involving the balance of carbonic acid H 2 CO 3 bicarbonate ion HCO and carbon dioxide CO 2 in order to maintain pH in the blood and duodenum among other tissues to. The bicarbonate buffer system is an effective buffer system despite having a low pKa because the body also controls pCO 2 224.
The bicarbonate buffer system is an acid-base homeostatic mechanism involving the balance of carbonic acid H 2 CO 3 bicarbonate ion HCO 3 and carbon dioxide CO 2 in order to maintain pH in the blood and duodenum among other. A buffer system exists to help neutralize the blood if excess hydrogen or hydroxide ions are produced. The carbonic acid - bicarbonate buffer system consists of carbonic acid a weak acid and the bicarbonate anion its conjugate base.
Delta pH with bicarbonate buffer or phosphate in the medium was greater at low than at high medium pH so that the difference delta delta pH between delta pH. The increased atmospheric CO 2 as a result of burning fossil fuels has driven this entire reaction to far to the right. Other Buffers The other buffer systems in the blood are the protein and phosphate buffer systems.
In the human stomach and duodenum the bicarbonate buffer system serves to both neutralize gastric acid and stabilize the intracellular pH of epithelial cells via the secretion of bicarbonate ion into the gastric mucosa. The important thing to realize here is that carbonic acid H2CO3 is actually formed when carbon dioxide CO2 is dissolved in water. True False Increasing alveolar ventilation increases extracellular fluid H concentration and decreases pH.
What would happen if the amount of CO 2 in the atmosphere were to sharply rise.

Chemical And Physiological Ph Buffers Nursing School Notes School Notes Chemical

Electrolyte Fluid Balance Nursing School Survival Respiratory Alkalosis Fluid And Electrolytes

Hydrostatic Pressure Capillary Filtration Pressure Capillary Colloidal Osmotic Pressure Pediatric Nurse Practitioner Nursing School Studying Nursing Study

Electrolyte Fluid Balance Nursing School Survival Respiratory Alkalosis Fluid And Electrolytes
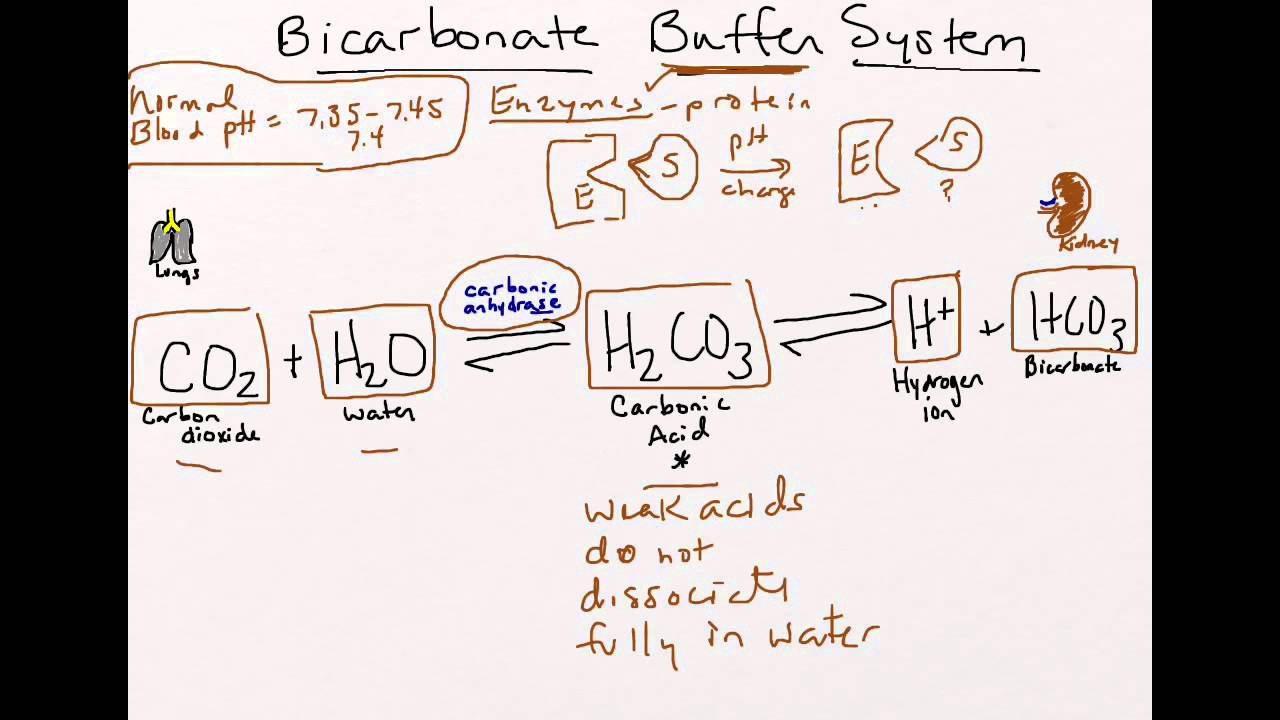
Bicarbonate Buffer System System Study Tips Pharmacy School

Bicarbonate Buffer System Example Of Multiple Equilibria Teaching Chemistry Medical School Studying Biochemistry

Description Diagram Of The Co2 Bicarbonate Physiological Buffering System Showing Equilibria Ka Values And Wonders Of The World Oceans Of The World Wonder

Mcat Favorite Vhy Bicarbonate Buffer System Buffer Respiratory System System






Posting Komentar untuk "Bicarbonate Buffer System"