Carbonate Titration Curve
This is the solubility product of calcium carbonate. The equations written in brown color are shown as dashed curves in the diagram below.

Titration Curve For A Mixture Of Hydroxide Silicate And Carbonate The Download Scientific Diagram
The titration curves will yield information on the buffering capacities of the waters the ions responsible for that buffering.
Carbonate titration curve. The shape of the pH titration curve will be observed and the Kb values for the base will be determined. The pH is initially 1300 and it slowly decreases as HCl is added. P Alk phenolphthalein alkalinity T Alk total alkalinity all alkalinity values are.
Chlorofluorocarbons and the environment. The longer you wait for equlibration near the the equlibrium point the more dissolved ceCO2 reacts to hydrogen carbonate and distorts your ideal ceCO2-free titration curve. Titration Results Bicarbonate Alkalinity Carbonate Alkalinity Hydroxide Alkalinity If P Alk 0 TAlk 0 0 If P Alk ½ T Alk TAlk 2P Alk 2P Alk 0 If P Alk ½ T Alk 0 2P Alk 0 If P Alk ½ T Alk 0 2T Alk PAlk 2P Alk - TAlk If P Alk T Alk 0 0 TAlk Key.
You will compare the pK a values for both phthalic acid and carbonic acid found in reference tables to those determined from your titration curves. Plot the titration curve for the titration of 120 mL of 220 mM potassium carbonate with 300 mM HNO 3. Figure 16-3 Titration curves and indicator transition ranges for the analysis of mixtures containing hydroxide carbonate and hydrogen.
These will be equal to the pH of the analyte solution at one half the equivalence volume of titrant added. NH is a weak base so the pH is above 7 but is lower than what we saw with a strong base NaOH case 1. Titration curves and Gran Function curves were then plotted for the upstream Figs.
Capacitors in electrocardiography monitors. This video shows the collection of pH data for the titration curve for sodium carbonate. Suppose you start with 25 cm 3 of sodium carbonate solution and that both solutions have the same concentration of 1 mol dm-3.
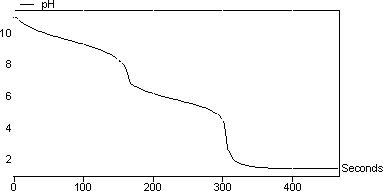
Another point where the calculated pH will be compared to the measured pH is the first equivalence point of the diprotic titration curve. Adding hydrochloric acid to sodium carbonate solution. At this point the amphoteric intermediate species is the only species present.
As the equivalence point is approached the pH drops rapidly before leveling off at a value of about 070 the pH of 020 M HCl. HCl and NaOH are strong acid and strong base respectively and their titration curves are similar shape of curve in different concentrations. Titration curve of strong acid and strong base.
Repeat your titration using methyl orange indicator instead of phenolphthalein. The discrepancies emerge when compared with exact calculations in the next diagram. Here are reduced versions of the graphs described above so that you can see them all together.
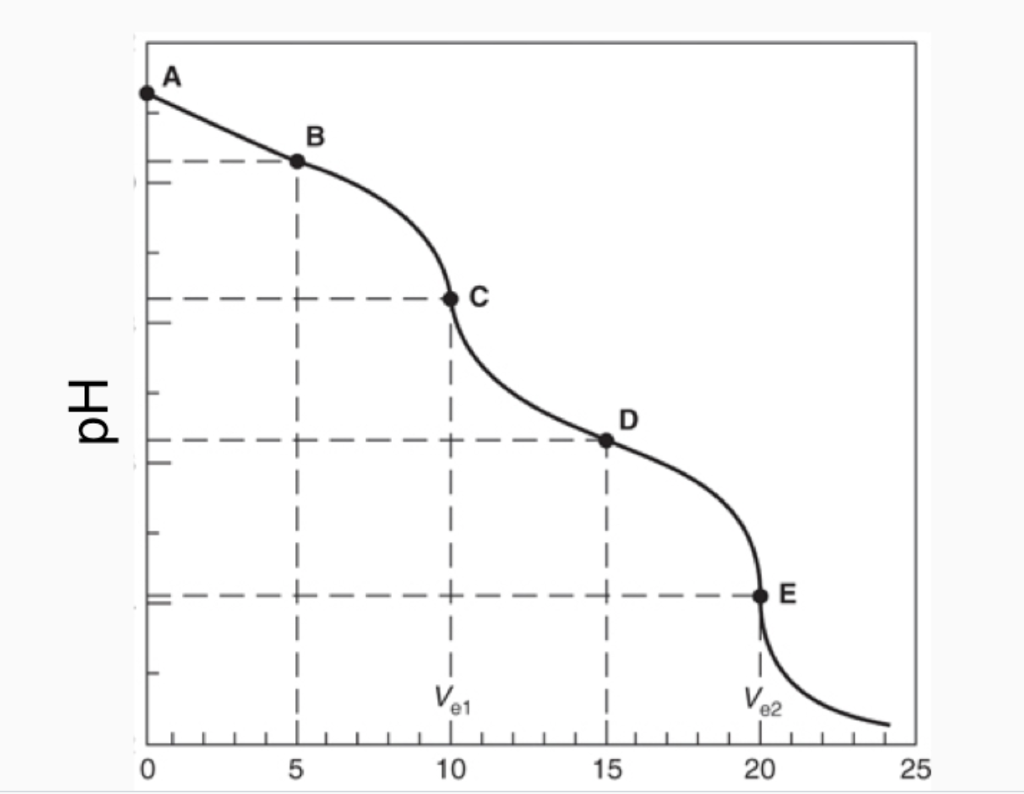
Titration of 1000 ml of hydroxide-carbonate mixture with 02062 HCl. A summary of the important curves. Equivalence point is the point in the titration here the amount of titrant added is enough to completely neutralize the solution.
A 200 mL of titrant B 500 mL of titrant C 880 mL of titrant D 1000 mL of titrant E 1300 mL of titrant F1760 mL of titrant. So the hydrogen ions attach to the carbonate one at a time. Electric Field Treatments and electroporation.
Titration of Sodium Carbonate with Hydrochloric Acid. From the results of these titrations you will calculate the concentrations of the various inorganic carbon species. For C T 10-7 M because the self-ionization of water is ignored.
Pipette out 2500mL of the given carbonate solution into a titration flask add few drops of phenolphthalein indicator and titrate the solution with 01M HCl. From the titration curves. The titration curve was plotted based on the data from the titration of HCl and aqueous sodium carbonate.
Then the curve was plotted with volume and PH value based on the experiment. That means that you would expect the steep drop in the titration curve to come after you had added 50 cm 3 of acid. NaOH HCl NaCl H 2 O.
In this experiment a solution of Na2CO3 will be titrated with a solution of HCl. The pH of the solution will be monitored as the HCl is added with a pH probe attached to a CBL. Part of NCSSM CORE collection.
Determine the pH after the following volumes of titrant have been added. More complicated titration curves. After the equivalence point NH addition continues and is in excess so the pH increases.
Charles law and gas in a piston. Electrostatics medicine and metal spheres. Titration curve for sodium carbonate and hydrochloric acid - YouTube.
Titration Curves A titration curve is a graph of the pH vertical axis versus the amount of the reagent progressively. Titration curve of strong acid weak base and strong acid strong base. The alkalinities for the samples were calculated using Equation 3.
5 6 and the Big Five Tunnel Figs. Both reactants and products are in aqueous state. The actual graph looks like this.
K CaCO Ca CO o CaCO 3 2 - 3 2 3 19. In the case of the carbonate CO 3 2- titration the intermediate species is hydrogen carbonate or bicarbonate HCO 3. 3 4 downstream Figs.
Ml titration curve b Gran function plots revealing three equivalence points 187 ml and two further segments of 103 ml each. To show you the impact more clearly I created the following figures showing both of your systems with varying carbonic acid concentrations left000ldots005. Collected in the first weeks of the term.
Please note that this approach is an approximation that works for almost all practical cases but fails at extremely low concentrations ie. The titration of either a strong acid with a strong base or a strong base with a strong acid produces an S-shaped curve. Important factors and equations of HCl NaOH reaction and its titration curve.
For the case of a fixed partial pressure of carbon dioxide and calcium carbonate dissolved in the aqueous phase one more equation is need to describe the system. Cardiac dysrhythmia and defibrillators. The way you normally carry out a titration involves adding the acid to the alkali.
The endpoint volume alkalinity and alkalinity as calcium carbonate for each sample are displayed in table 2. Calcium carbonate in water with a fixed partial pressure of carbon dioxide. We use the second reaction equivalence point because we want the pH value when the reaction is complete.
Science Experiment Acid Base Titrations Results

Ap Lecture 3 11 Weak Base Strong Acid Titration Youtube

Which Make Hco3 To Show Two Ph Values At Two Scenarios Chemistry Stack Exchange

The Theoretical Titration Curves And Gran Functions For Titration Of Download Scientific Diagram

The Titration Curve And Gran Functions For Titration Of The A Download Scientific Diagram

Titration Of Sodium Carbonate With Hydrochloric Acid Youtube

The Titration Curve And Gran Functions For Titration Of The A Download Scientific Diagram

During The Titration Of Sodium Carbonate With H Cl The Dissolved Carbonate Ion Will Exist In Three Different Forms Co 3 2 H Co 3 1 And H 2 Co 3 During Which Part Of The Titration Initial
Ph Curves Titration Curves Chemkey

Which Make Hco3 To Show Two Ph Values At Two Scenarios Chemistry Stack Exchange
Ph Curves Titration Curves Chemkey
Solved In The Titration Curve Of Carbonate With Strong Acid Chegg Com


Posting Komentar untuk "Carbonate Titration Curve"