Carbonate Bicarbonate Equilibrium
CO2g H2O CO2aq H2O 94 CO2aq H2O H2CO3 95 where g and aq refer to the gaseous and dissolved phase respectively. For this reason most running waters are bicarbonate waters in a limnological sense and show the complicated relationships between.

Which Formula Can Be Used To Calculate The Exact Hydronium Concentration Present In Sodium Hydrogen Carbonate Solution Chemistry Stack Exchange
All of the CO 2-derived chemical species in the water together ie.
Carbonate bicarbonate equilibrium. This carbonic acid-carbonate equilibrium determines. Physico-chemical characteristicsstudy of natural waters like that behaviour on environmental background is very often deal with specific cases for the complexity sake of relations between present ions. The next sections will be devoted to analysing the chemical composition of carbonate waters.
In aqueous solution carbonate bicarbonate carbon dioxide and carbonic acid exist together in a dynamic equilibrium. Likewise if a strong base is introduced it will react with the carbonic acid to form the bicarbonate anion thus reducing the potential increase in pH. As we know the pH and K2 we can calculate the ratio between carbonate and bicarbonate.
CALCIUM CARBONATE-CARBONIC ACID EQUILIBRIUM. From the equilibrium we have. It can be seen from the calibration spectrum that there are completely visible independent nicely shaped peak assigned to each other.
CO 2 g H 2 O l H 2 CO 3 aq HCO 3 aq H aq The system is at equilibrium when it is a closed system the reactions are reversible and the rate of the products being formed is equal to the rate of reactants being formed. However this may be not true when it comes to the real. Major buffer system influencing pH master variable Linked to geological biological and climatological cycles Complex chemistry involving gaseous dissolved and solid phases Cycle undergoing significant anthropogenic perturbation mostly from fossil fuel burning Oceanic Carbonate System controls.
Carbonate Equilibria and log K Values. PH C02 H2CO3 H C03 HCO3- calcium 2 and magnesium 2. Catalyzed by carbonic anhydrase carbon dioxide reacts with water to form carbonic acid which in turn rapidly.
The basic equations for the open and closed carbonate systems are well understood and described in many textbooks. The CarbonateBicarbonate buffer system is an important way for the ocean to maintain chemical equilibrium. 2 aq CO.
By making the appropriate substitutions we can rewrite this in terms of H the bicarbonate ion concentration and the various equilibrium constants. Implicit in this statement is the relationship among dissolved carbonate species whether or not they are in equilibrium with solid phase metal carbonates. What would happen if the amount of CO 2 in the atmosphere were to sharply rise.
The equilibrium will thus shift to the left. CO 2 K H p CO2 H 3 CO 2 2 K a1 2 K a22K sp. Using the equations above it is possible to calculate the concentration of any of the species in solution.
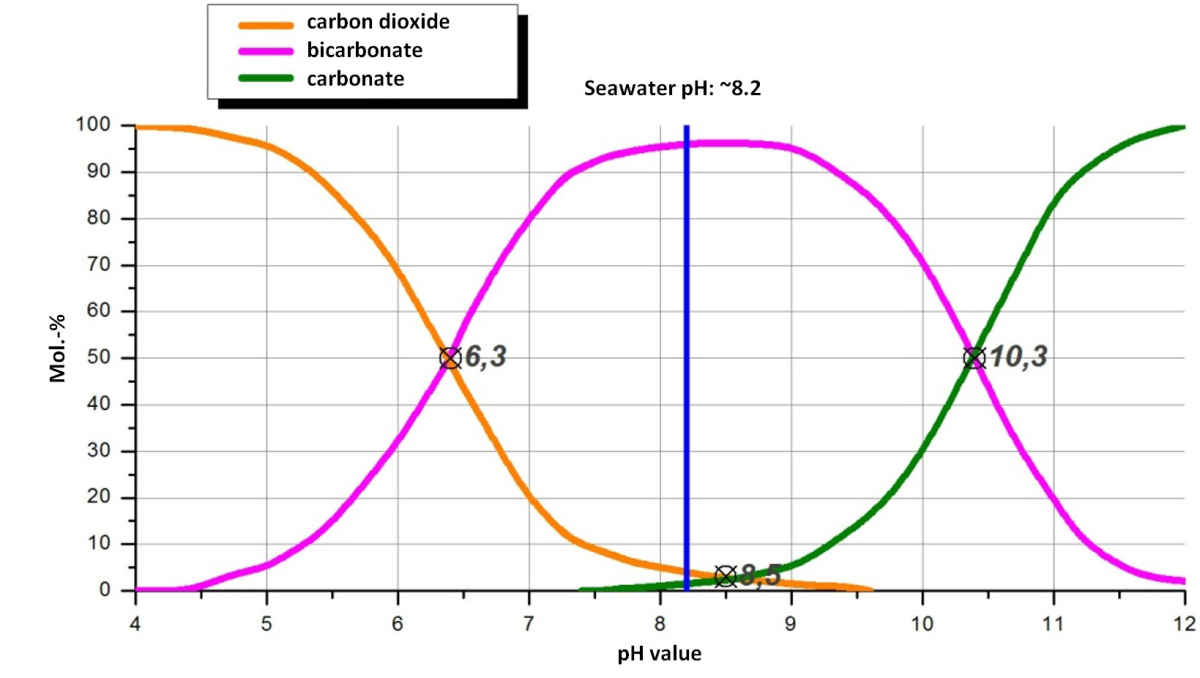
About 90 of this is present as bicarbonate ion the proportion of carbonate ion is about a factor of 10 less 10 and that of unionised carbon dioxide yet another factor of 10 less. The carbonate equilibrium which includes free CO 2 or carbonic acid bicarbonate ions and carbonate ions is highly pH dependent. Interactions among these compounds determine the conditions under which limestones and dolomites are fomied or dissolved and likewise the conditions of formation of carbonate minerals as.
Carbon dioxide carbonic acid bicarbonate and carbonate ions are referred to as dissolved inorganic carbon DIC. H K 2CO 2 3 H K w H OHHCO 3 K 1 Chem1 Environmental Chemistry 5 Carbonate equilibria in natural waters. The increased atmospheric CO 2 as a result of burning fossil fuels has driven this entire reaction to far to the right.
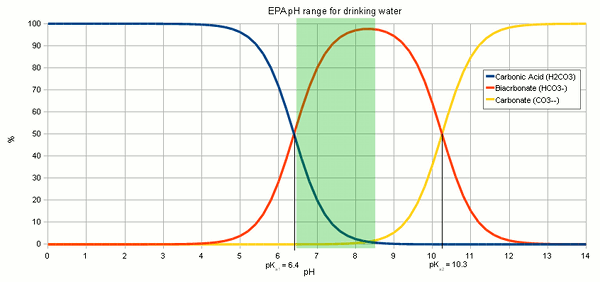
In strongly basic conditions the carbonate ion predominates while in weakly basic conditions the bicarbonate ion is prevalent. For every one mole of hydronium relative to bicarbonate we have two moles of hydronium relative to carbonate. The CO 2 bicarbonate equilibrium exists in the pH range of 43 to 83 and the bicarbonate carbonate equilibrium dominating at pH 83 123.
The carbonate reacts with CO 2 to form bicarbonate which leads to a further uptake of CO 2 and a decline of the CO 3 2 concentration in the ocean. The NH 3-CO 2-H 2 O system consists of several equilibrium reactions and the compositions of carbonate bicarbonate and carbamate are influenced by the concentrations of each other. So in a weird way by increasing our pH to become hydronium deficient equilibrium shifts towards the intuitively lower pH side of the reaction to try and counteract this and we get carbonate as a byproduct.
This is the general equilibrium equation that describes the carbonic acid bicarbonate system. Carbonate Equilibria If other sources of these species are present in the solution - for example dissolved CaCO. Carbonic acid and the carbonate minerals provide another good illustration of the use of equilibrium reasoning in geochemistry.
The concentration of calcium carbonate is governed by the solubility product constant of the mineral. PH pK2 logfracceHCO3-CO32- This is the old HendersonHasselbalch equation you surely heard about before. This means that there is an excess of.
Section 5- Carbonate Chemistry CARBONATE EQUILIBRIA Carbonates are arguably the most important dissolved component of soil solutions and in alkaline soils this statement is even less disputable. This equilibrium is unstable behaviour due to variation of temperature and dissolved. 3 s Ca.
From limestone or sea shells - then these must also be taken into account in finding the concentrations. Magnesium are normally accompanied with carbonate alkalinity. 92 CARBONIC ACID EQUILIBRIA In the presence of gaseous CO2 dissolved CO2 exchanges with CO2 gas.
Bicarbonate ion carbonate ion and unionised dissolved carbon dioxide is only about 2 mmol kg1. Carbonate Equilibrium -Key Concepts-. K a2 CO 3 2-H HCO 3- 10-84.
K sp Ca 2CO 3 2- 10-83. Carbonates are perhaps the most important dissolved components in natural waters. A process for producing sodium carbonate and other sodium-based chemicals from an aqueous solution containing sodium bicarbonate by contacting an aqueous solution of a bicarbonate-containing composition with a gas that is predominately other than carbon dioxide in an amount and for a time adequate to cause a sufficient amount of carbon dioxide to leave the aqueous.
Bicarbonate is also an acid. The equilibrium will. CeH3O fracceK2HCO3-ceCO32- Or in logarithimic form.
The bicarbonate buffer system is an acid-base homeostatic mechanism involving the balance of carbonic acid bicarbonate ion and carbon dioxide in order to maintain pH in the blood and duodenum among other tissues to support proper metabolic function. The fact that a strong acid is converted to a weak one will prevent to acidity of the solution to increase significantly. As will be discussed in alkalinity it is important to note that bicarbonates tend to reach equilibrium with the carbonates.
As a result of the. However the nomenclature differs sometimes considerably especially when thermodynamic data from different databases are.

Shwetaak Grade 12u Chemistry Systems And Equilibrium

Carbon Dioxide Equilibrium In Water Aqueous Systems Zimmerandpeacock

Alkalinity Reduction With Slaked Lime German Brewing And More

Carbonate Alkalinity Vs Corrected Alkalinity
Ph Dependence Of The Dissociation For The Reaction Of Bicarbonate Download Scientific Diagram

The Carbonate Equilibria Equations And The Corresponding Equilibrium Download Table

Chemistry Microscopesandmonsters

Dependence Of Bicarbonate And Carbonate Ion Concentration On Ph Graph Download Scientific Diagram
Carbonate Co2 Scrubbing Process Ii Eco2 Practical Experience And Technical Optimisation Cement Lime Gypsum



Posting Komentar untuk "Carbonate Bicarbonate Equilibrium"