Carbonate Equilibrium
The calculation is based on simplified carbonate equilibria including dissolved CO 2 bicarbonate ion HCO 3 carbonate ion CO 3 2 hydrogen. All of the CO 2-derived chemical species in the water together ie.

Simple Method For Writing Lewis Structures Ozone O3 And Carbonate Co3 2 Molecular Geometry Writing Chemistry
Carbonate Equilibria and log K Values.

Carbonate equilibrium. The carbonate reacts with CO 2 to form bicarbonate which leads to a further uptake of CO 2 and a decline of the CO 3 2 concentration in the ocean. However the nomenclature differs sometimes considerably especially when thermodynamic data from different. They must sum to 1100 as in chemical reactions matter is neither created or destroyed only changing between forms.
Once this basic seawater chemistry has been presented and assimilated it will be appropriate to revisit a. Interactions among these compounds determine the conditions under which limestones and dolomites are fomied or dissolved and likewise the conditions of formation of carbonate minerals as. AC HCO3 2CO 3 2 b 2c 915 If the water contains Ca2 or Mg2 and carbonate or is in contact with calcite also the dissociation equilibrium of calcite affects the carbon chemistry.
K w HOH- 10-14 M2 Note. Carbon dioxide carbonic acid bicarbonate and carbonate ions are referred to as dissolved inorganic carbon DIC. CaCO 3s Ca2aq CO 3 2-aq K sp Ca2CO 3-2 447109 mole2liter2 in fresh H 2O.
CO 2g CO 2aq Subsequent hydration and dissociation reactions. K sp Ca 2CO 3 2- 10-83. This carbonic acid-carbonate equilibrium determines.
Carbonate Equilibrium -Key Concepts-. The concept of calcium carbonate saturation state will also be introduced. K 1 HCO 3-HH2CO 3 9 x 10-7 M 10-61 M 3.
CO 2aq H 2O H 2CO 3 HCO 3- H HCO 3- CO 3-2 H Hint. Major buffer system influencing pH master variable Linked to geological biological and climatological cycles Complex chemistry involving gaseous dissolved and solid phases Cycle undergoing significant anthropogenic perturbation mostly from fossil fuel burning Oceanic Carbonate System controls. CaHCO32NaClH2O within the range of alkalinity of 00005 molkg and temperatures of 025C.
When pH is between 75 and 85. Carbonate equilibrium reactions Why important Alkalinity Chemical weathering Diurnal changes in DO and pH Whats up. Constants are sensitive to temperature and ionic.
CO 2 K H p CO2 H 3 CO 2 2 K a1 2 K a22K sp HCO 3- CO 2K a1H 2 K spH 2K a1K a2CO 2. Basic chemical reactions for the carbonate system are presented including equilibrium expressions for each reaction and discussion about open and closed systems. Carbonates are perhaps the most important dissolved components in natural waters.
Carbonates are readily decomposed by acids. K 2 CO 3 2-HHCO3- 27 x 10-10 M 10-96 M4. The carbonate equilibrium system is a system in which there is exchange of C03 z- C02 and HC03-.
The basic equations for the open and closed carbonate systems are well understood and described in many textbooks. This changes how ANC is calculated and the ANCp. Implicit in this statement is the relationship among dissolved carbonate species whether or not they are in equilibrium with solid phase metal carbonates.
Carbonate is a carbon oxoanion. Values of these equil. Carbonic acid and the carbonate minerals provide another good illustration of the use of equilibrium reasoning in geochemistry.
The concentration of calcium carbonate is governed by the solubility product constant of the mineral. This system also helps to keep the oceans buffered between the pH of 76 to 82. It is a conjugate base of a hydrogencarbonate.
This web app calculates the partial pressure of CO 2 pCO 2 and pH of seawater in equilbrium with the atmosphere given sea-surface temperature titration alkalinity and dissolved inorganic carbon. The equilibrium of gaseous and aqueous CO 2. Solubility of CO 2 and Carbonate Equilibrium 1.
And the equilibrium mixture the latter is designated by H 2CO 3 2. HHCO 3 H 2CO 3 K 1 1063 5 HCO2 3 HCO 3 K 2 10103 6. In the second part a presentation on chemical equilibrium for the carbonate system is given.
Carbonate Equilibrium System Explanation. Magnesium are normally accompanied with carbonate alkalinity. The carbonate equilibrium which includes free CO 2 or carbonic acid bicarbonate ions and carbonate ions is highly pH dependent.
Using the equations above it is possible to calculate the concentration of any of the species in solution. It is very common that calcium carbonate - limestone - is in contact and in equilibrium with natural waters. Partial pressure of carbon dioxide that is in equilibrium with a water sample Box 11.
Photosynthesis is the biochemical process in which plants and algae harness the energy of sunlight to produce food. The starting point is the answers received in the first part. By an acid titration referred to as the total alkalinity thus about equals the carbonate alkalinity defined as.
The Pitzer technique was employed to calculate the apparent constants of carbonate equilibrium in solution that models the riverine water. In a saturated solution of calcium carbonate the rate of solution and the rate of precipitation are equal so the system is at equilibrium. The equilibrium constant for this process is called the solubility product K sp.
K H H 2CO 3P CO2 3 x 10-2 M atm-1 10-15 M atm-1 2. The CO 2 bicarbonate equilibrium exists in the pH range of 43 to 83 and the bicarbonate carbonate equilibrium dominating at pH 83 123. CO 2aq CO 3-2 H 2O 2HCO 3- 2 3 1 CO H HCO K 3 2 3 2 HCO H CO K Asterisk indicates a stoichiometric constant CO.
When the calcium carbonate dissolves a equilibrium is established between its three forms expressed by the respective equilibrium equations. Water exposed to the atmosphere with P CO 2 10 35atm will take up carbon dioxide until from Eq 2 H 2CO 310 151035 105M 4 The following equilibria are established in any carbonate-containing solution. Carbonate Ion is a polyatomic ion with formula of CO3 2-.
Photosynthesis of aquatic plants and algae in the water. Salts or ions of the theoretical carbonic acid containing the radical CO2 3-. Section 5- Carbonate Chemistry CARBONATE EQUILIBRIA Carbonates are arguably the most important dissolved component of soil solutions and in alkaline soils this statement is even less disputable.
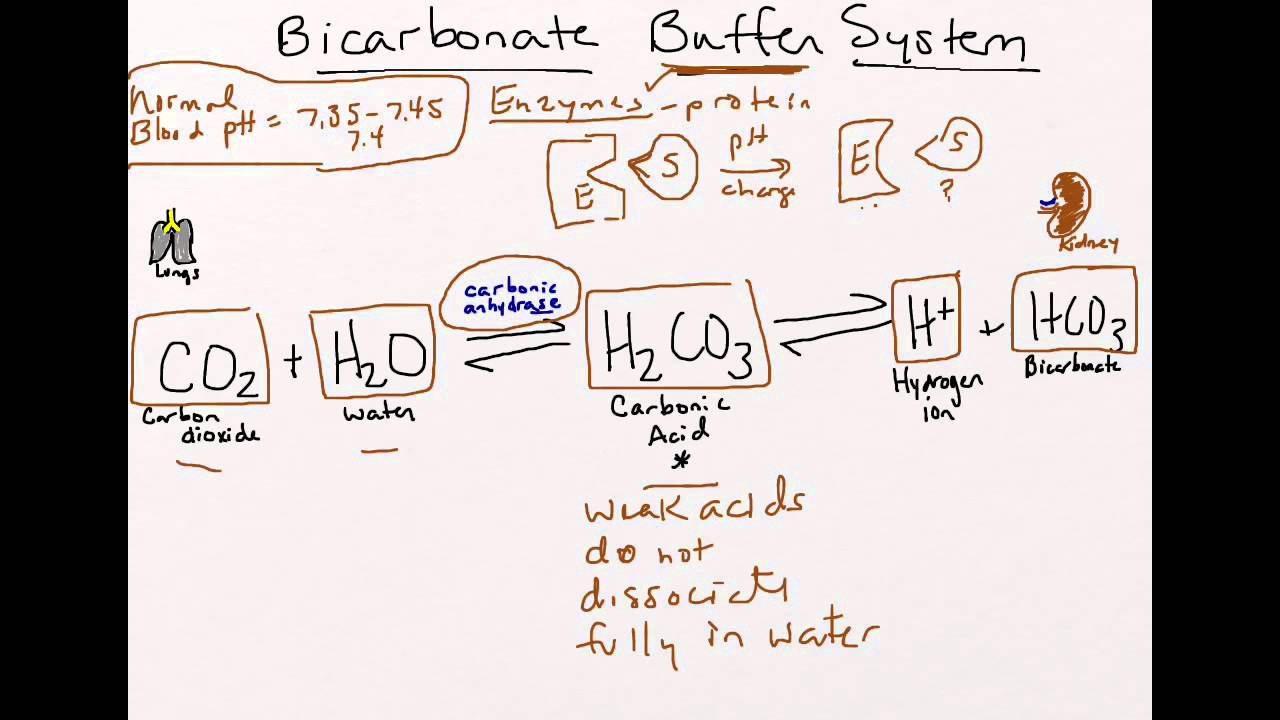
Bicarbonate Buffer System System Study Tips Pharmacy School

Ocean Acidification Ocean Acidification Marine Organism Young Animal

Law Of Mass Action Chemical Equilibrium Chemistry Animation Chemistry Lessons Chemistry Equilibrium

13 1 Chemical Equilibria Chemistry Libretexts Stem Projects Equilibrium Chemistry

Hummocky And Swale Crossbedding Geology Geophysics Sedimentary Rocks

Chemical Equilibrium Characteristics Types Examples Constant Equilibrium Chemical Chemistry

Effect Of Sodium Carbonate On Foaming Capacity Of A Soap Chemistry Project Experimen Chemistry Science Fair Projects Chemistry Projects Science Fair Projects

Acids And Bases Teaching Chemistry Chemistry Review Chemistry

Stoichiometry Ii Chemical Equations 03 Gif 600 211 Pixels Teaching Chemistry Chemistry Education Science Chemistry

Pin By Marco Antonio On Chemistry Chemistry Class Chemistry Problem Solving




Posting Komentar untuk "Carbonate Equilibrium"