Carbonate Buffer System Explained
Other buffers perform a more minor role than the carbonic-acid-bicarbonate buffer in regulating the pH of the blood. In the body a bicarbonate buffer system is used to regulate the pH of blood.
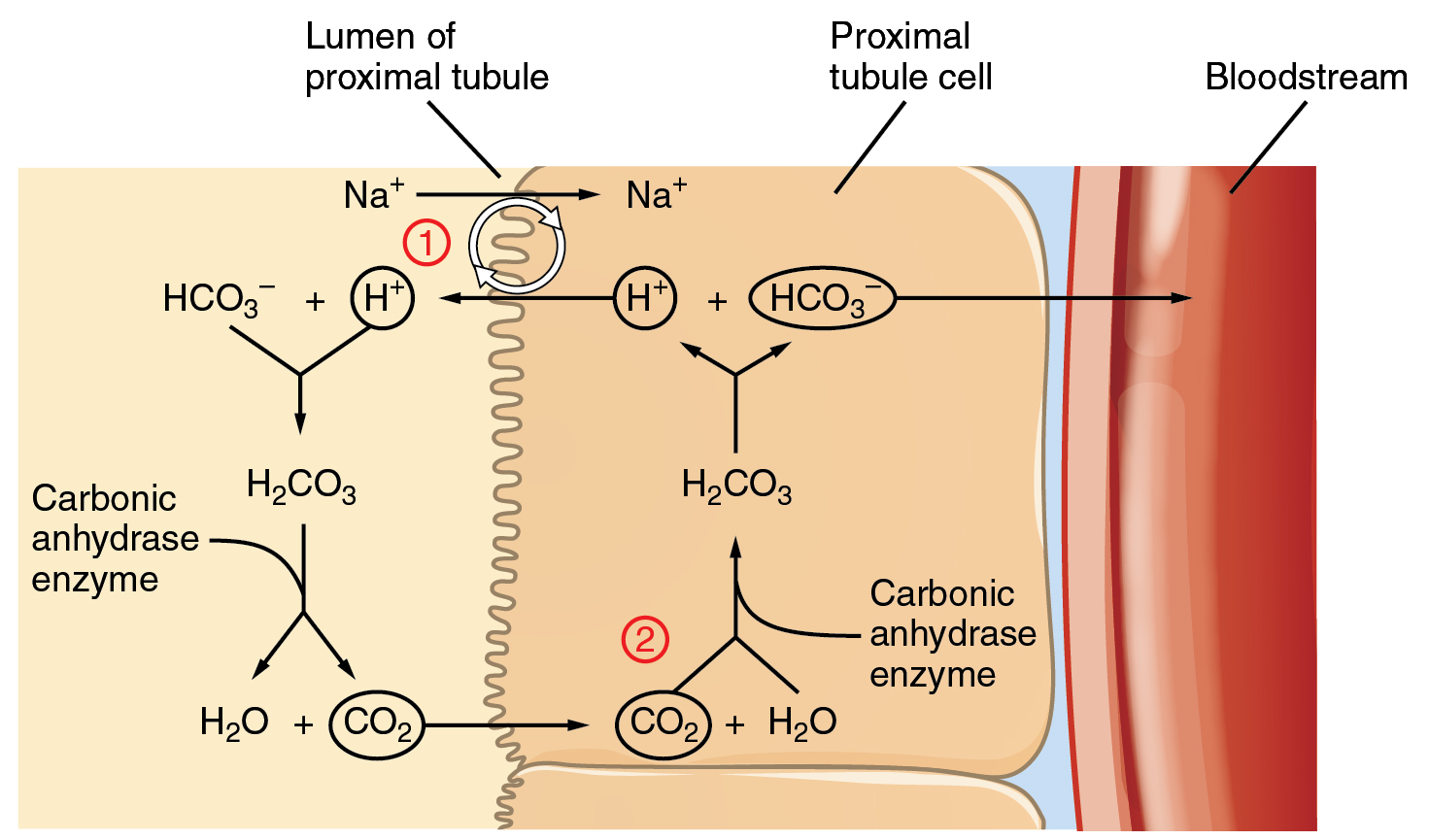
Acid Base Balance Anatomy And Physiology
Carbonate Buffered solution 01M Sodium Bicarbonate-Sodium Carbonate Buffer pH 90 UPR16490 250 ml - Applications.

Carbonate buffer system explained. The buffer system is comprised primarily of bicarbonates and carbonates giving the buffer system the alternative name of Carbonate Hardness. A buffer system has the property of resisting pH changes despite additions of acid or base. For example if the final mobile phase pH is 43 acetate is all that is needed so phosphate does not need to be used at all.
Coating protein oon microplates. Explained using Bronstead-Lowry acid base reactions When a strong acid is added to the buffer. This is a buffer this is a buffer system.
Some analysts like to use citrate for a buffer because it has three overlapping pKa values that allow buffering over the 21. While the third buffer is the most plentiful the first is usually considered the most important since it is coupled to the respiratory system. The respiratory and renal systems also play major roles in acid-base homeostasis by removing CO 2 and hydrogen ions respectively from the body.
Sodium Carbonate Anhydrous ACS grade 141321 1 Kg 141322 25kg 141321 MW. That is it can undergo two de-protonation reactions to form bicarbonate HCO 3- and carbonate CO 3 2-. The major feature of the bicarbonate buffer is the capacity of the body to easily eliminate both the Weak Acid and the Weak Base form of the buffer in an independent fashion.
Consequently the body can gain exquisite control over the ECF pH simply by modulating elimination of either HCO 3 - Weak Base or CO 2 Weak Acid. The pK for the phosphate buffer is 68 which allows this buffer to function within its optimal buffering range at physiological pH. When the first proton is donated HCO3- otherwise known.
K CaCO Ca CO o CaCO 3 2 - 3 2. The carbonatecarbonic acid buffer the phosphate buffer and the buffering of plasma proteins. The main role of the bicarbonate system is to regulate and control the pH of blood and counteract any force that will alter the pH.
Potassium Chloride KCl 11-18. Buffers in the pH. Carbonic acid is divalent.
Once you find the desired pH the buffer not needed can be eliminated. Carbonate System 1 1 MAR 510 Chemical Oceanography Carbonate Equilibrium-Key Concepts- Major buffer system influencing pH master variable Linked to geological biological and climatological cycles Complex chemistry involving gaseous dissolved and solid phases Cycle undergoing significant anthropogenic. When atmospheric carbon dioxide is dissolved in seawater carbonic acid H 2 CO 3 is formed.
If youre seeing this message it means were having trouble loading external resources on our website. Hydrochloric Acid - HCl 0-2. Another name for the buffer system is the total alkalinity.
Recall that buffers are mixtures of weak acids and their conjugate bases that resist changes in pH. The role of the bicarbonate buffer system in regulating blood pH practice Khan Academy. Perchloric Acid HClO.
Buffer pKa and pH Range Values For preparation of. Oxalic Acid C. One that is important in surface waters is the carbonic acidbicarbonate buffer.
When cola is added to the above buffer system. For the case of a fixed partial pressure of carbon dioxide and calcium carbonate dissolved in the aqueous phase one more equation is need to describe the system. The bicarbonate buffer is the primary buffering system of the IF surrounding the cells in tissues throughout the body.
However other bases such as hydroxides silicates phosphates and borates contribute to the buffering capacity. Calcium carbonate CaCO3 is a very common mineral. Human blood contains a buffer of carbonic acid H 2 CO 3 and bicarbonate anion HCO 3- in order to maintain blood pH between 735 and 745 as a value higher than 78 or lower than 68 can lead to death.
The Carbonic AcidBicarbonate Buffer. Because these equilibrium reactions between carbon dioxide carbonic acid and bicarbonate this is a buffer system. The important thing to realize here is that carbonic acid H 2CO3 is actually formed when.
An explanation of how the bicarbonate buffer system function into respiratory and metabolic pH imbalances-- Created using PowToon -- Free sign up at httpw. Biological Functions of Buffers carbonic acidhydrogen carbonate buffer in the blood CO 2g H 2O l H 2CO 3aq May 06 2013. This is the solubility product of calcium carbonate.
Nitric Acid - HNO. A Brief Summary of Carbonate Buffer System Chemistry Atmospheric CO 2 dissolves in seawater and is hydrated to form carbonic acid H 2 CO 3. Buffers pKa range.
Carbon dioxide plays a vital role in the chemistry of sea water. A buffer system exists to help neutralize the blood if excess hydrogen or hydroxide ions are produced. In this buffer hydronium and bicarbonate anion are in equilibrium with carbonic acid.
True False Increasing alveolar ventilation increases extracellular fluid H concentration and decreases pH. A buffer is a mixture of an acid that does not ionize completely in water and its corresponding base-for example carbonic acid H 2 CO 3 and sodium bicarbonate NaHCO 3. O system Calcium carbonate in water with a fixed partial pressure of carbon dioxide.
Furthermore the carbonic acid in the first equilibrium. And the word buffer in our everyday language it refers to something that kind of smooths the impact of something or it reduces the shock of something. Carbonic acid is diprotic which means in has two H ions to donate to solution.
In natural systems there are many buffers. 497-19-8 Sodium Carbonate Anhydrous Reagent Grade 08499A 1 Kg - MW. The bicarbonate buffering system is an crucial buffer system in the acid-base homeostasis of all living things.
The phosphate buffer consists of phosphoric acid H 3 PO 4 in equilibrium with dihydrogen phosphate ion H 2 PO 4- and H. To log in and use all the features of. The carbonic acid - bicarbonate buffer system consists of carbonic acid a weak acid and the bicarbonate anion its conjugate base.
The bodys chemical buffer system consists of three individual buffers. The CarbonateBicarbonate Buffer System.

Carbonate An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Mcat Question Of The Day The Bicarbonate Buffer System Youtube

Specific Plant Ph Infographic Hydroponicsinfographic Hydroponicstips Hydroponicgardening Hydroponicsorgan Aquaponics System Aquaponic Gardening Hydroponics

Acid Base Balance Anatomy And Physiology Ii
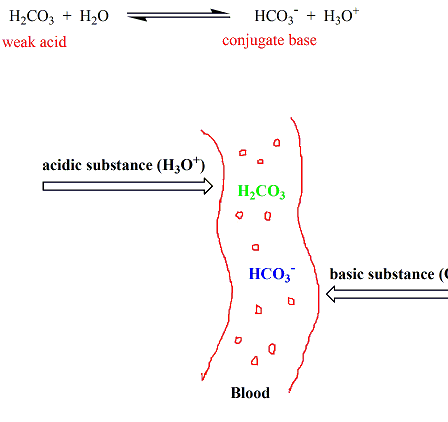
Chemistry Of Buffers And Buffers In Our Blood Article Khan Academy

Relationship Between Bicarbonate Buffer System And Carbon Dioxide Download Scientific Diagram

Aquaponics Ph Explained How To Maintain The Perfect Balance Aquaponics Solid Shampoo Bar Well Water System

Acid Base Balance Bicarbonate Ion Buffer Youtube
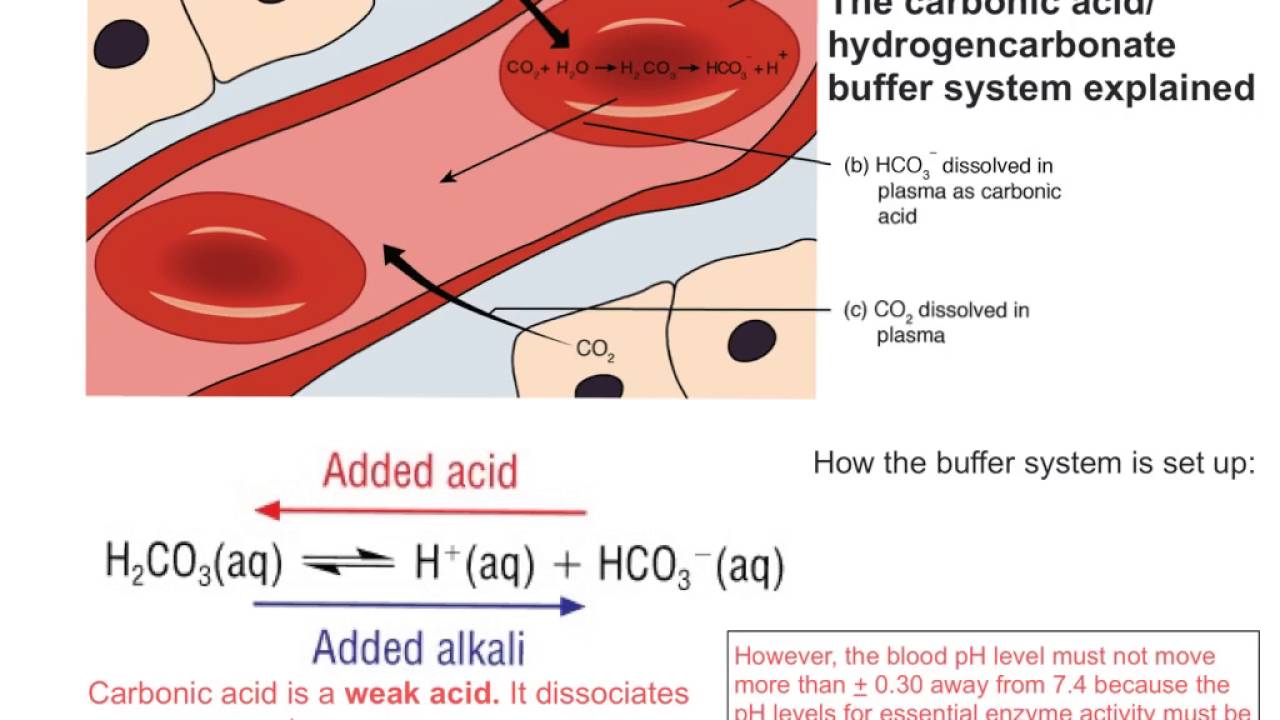
Buffer Action In The Blood Youtube

Chemical Buffers Protein Buffer Phosphate Buffer System And Bicarbonate Buffer System Youtube
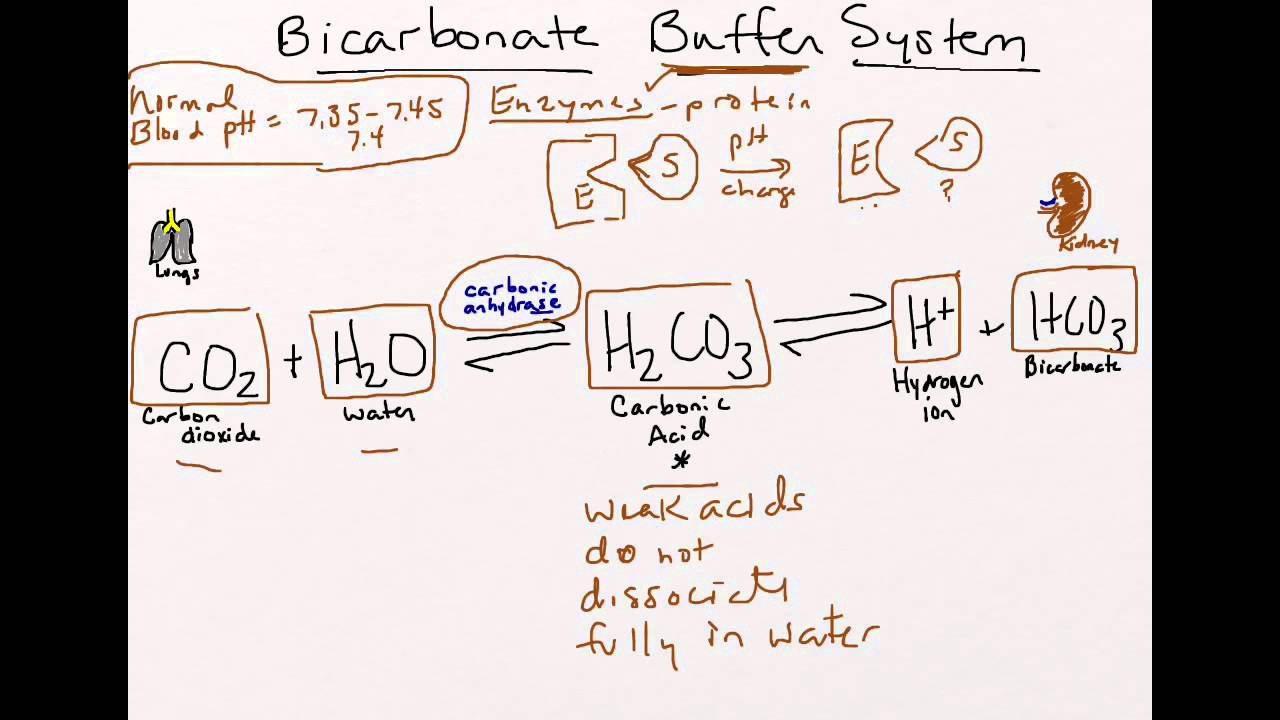
Bicarbonate Buffer System Youtube

Chemical Buffer Systems And Acid Base Balance

Posting Komentar untuk "Carbonate Buffer System Explained"