Carbonate Definition Geology
In the photo at left the orange-brown material is a carbonate cement binding pebbles of chert CT and quartz Q. Two major types are limestone which is composed of calcite or aragonite different crystalline forms of CaCO3 and dolostone which is composed of the mineral dolomite CaMg CO32.
The depositional environments described are made up of pure carbonate and evaporite deposits that do not contain terrigenous clastic or volcaniclastic material.
Carbonate definition geology. Jump to navigation Jump to search. In chemistry a carbonate is a salt of carbonic acid H 2 CO 3 characterized by the presence of the carbonate ion a polyatomic ion with the formula of CO 2 3. Carbonate reservoirs can be difficult to develop for a variety of reasons.
Carbonates are a set of minerals made of carbon oxygen and a metal element. Calcium carbonate dolomite calcium magnesium carbonate gypsum calcium sulfate dihydrate and salt halite. Since the definition of cavern is a cave formed in a soluble rock with the ability to grow speleothems the composition of a.
There are however modern environments where the sediments are mixtures of carbonate and other clastic materials and in the stratigraphic record. Geology of carbonate reservoirs PDF Geology of carbonate reservoirs Muhammad Waqas Siddiqui - Academiaedu Academiaedu no longer supports Internet Explorer. Carbonate platforms are buildups of carbonate rocks in the deeper parts of the oceans on top of continental blocks left behind during continent - continent separation.
In chemistry a carbonate is an ion consisting of one carbon and three oxygen atoms or a compound that contains this species as its anion. The name may also refer to a carbonate ester an organic compound containing the carbonate group COO 2. Noun ˈkɑːbəˌneɪt -nɪt a salt or ester of carbonic acid.
Carbonate ramp succession. A succession built up by the progradation of a carbonate ramp is characterised by an overall coarseningup from carbonate mudstone and wackestone deposited in the outer ramp environment to wackestones and packstones of the mid-ramp to packstone and grainstone beds of the inner ramp. Examples of carbonate rocks.
In geology carbonates are a class of sedimentary rocks compose primarily of carbonate minerals. Tr to treat with carbon dioxide or. All classifications of limestone s are arbitrary and they frequently overlap or do not fit ones particular needs.
Term introduced by Folk 1965 for carbonate particles that have formed by chemical or biochemical precipitation. Jeffrey Dravis is a carbonate geologist with 35 years of experience and owner of Dravis Geological Services which conducts exploration and reservoir development projects in the US Canada and overseas. There are are many studies published in books papers about carbonate.
Geology. The main groupsare fossil fragments ooids pellets intraclasts. See larger photo by USGS.
A combination of depositional geometry and diagenesis creates highly heterogeneous reservoirs Table 1. The two commonly go hand-in-hand. Carmel Formation Middle Jurassic of southern Utah USA.
A solid precipitate of calcium carbonate silica iron oxide clay minerals or other materials that forms within the pore spaces of a sediment and binds it into a sedimentary rock. One part involves mineral dissolution the other precipitation. Largest is 10 mm in diameter.
This calcite referred to as calcium carbonate is the maximum common of the carbonate group. A particle composed of multiple crystals. Carbonate diagenesis is like a game of two halves.
Reef building organisms from the framework of most of these carbonate buildups. Rock s are classified in order to communicate inform ation about them. Carbonate ooids on the surface of a limestone.
He specializes in unravelling the controls on diagenesis and porosity evolution in carbonate sequences that aid in exploiting. Carbonate rock any rock composed mainly of carbonate minerals. Mixed carbonate-clastic environments.
Since binocular microscopes or hand lenses are the tools that are commonly available to the explorationist a practical classification. Carbonate salts contain the divalent ion CO 3 2. Alternatively the term may be used as a.
Verb ˈkɑːbəˌneɪt to form or turn into a carbonate. Carbonate rock is sedimentary rock composed of at least 50 of carbonates aragonite calcite or dolomite. The diagrams and images of carbonate crystal habits and cements are descriptive and intended to provide essential background to other posts that detail the different diagenetic environments.
Modern carbonate sediments deposited in shoal-water shallow-water marine environments including shelves banks lagoons and coral reef tracts are predominantly biogenic in origin derived from the skeletons and tests of benthic and pelagic organisms such as corals foraminifera echinoids mollusks algae and sponges. Class of sedimentary rock. Carbonate rocks are a class of sedimentary.
The principal members of the group are the sedimentary rocks dolomite and limestone qqv. The molecular formula for the carbonate ion is CO 3 2-. They generally have poorer recoveries than siliciclastic sediments eg Sun and Sloan.
Many carbonate reservoirs offer a challenge to the production geologist.

Learning Geology Carbonate Platforms
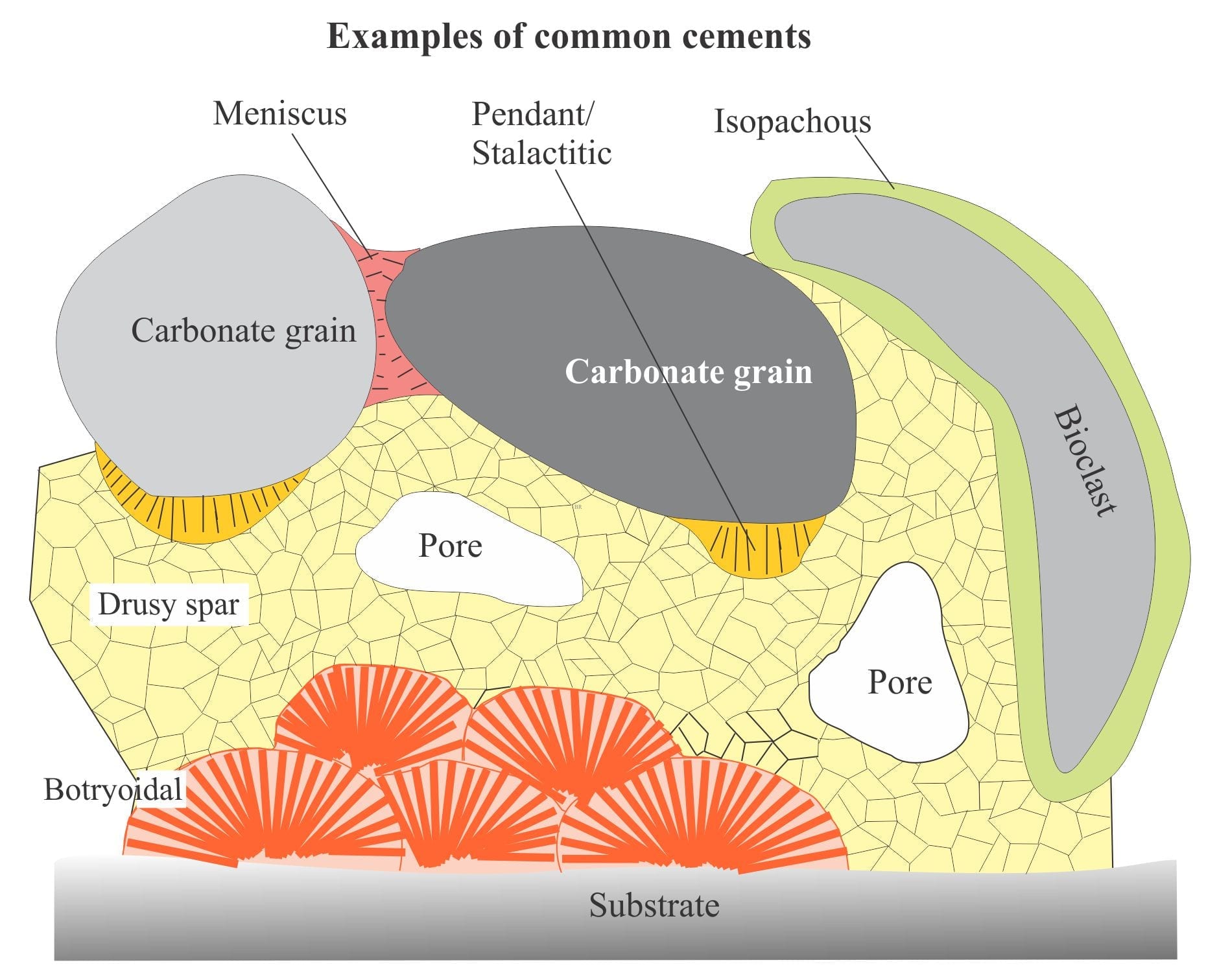
Mineralogy Of Carbonates Cements Geological Digressions

Learning Geology Carbonate Platforms
Carbonate Classification Sepm Strata

Geology Of Carbonate Reservoirs The Identification Description And Characterization Of Hydrocarbon Reservoirs In Carbonate Rocks Wiley
Diagenesis And Porosity Sepm Strata
Carbonate Classification Sepm Strata
Carbonate Classification Sepm Strata

Learning Geology Carbonate Platforms
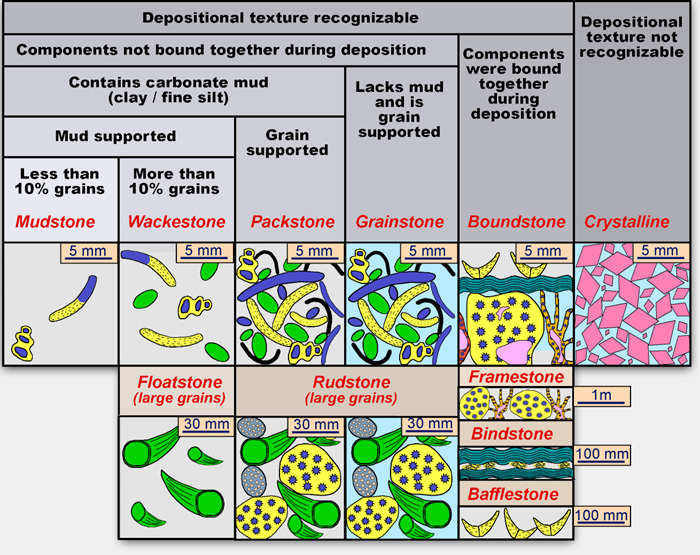
Introduction To Carbonate Facies Depositional Environments And Depositional Systems Dunham S Carbonate Rock Texture Classification
Carbonate Classification Sepm Strata
Posting Komentar untuk "Carbonate Definition Geology"